Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tateishi, Ryo*; Shimada, Koji; Iwamori, Akiyuki*; Wada, Shinya*; Seno, Shotaro*; Nagata, Ken*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi (Internet), 128(1), p.63 - 64, 2022/04
The Tsuruga Fault is an active right-lateral strike-slip fault that is about 20 km in length and distributed in the northeast-southwest direction from the eastern part of Tsuruga City to the southern part of Mihama Town, Fukui Prefecture. The Tsuruga fault borders the Jurassic accretionary complex (mixed rock) and the late Cretaceous granite around the Oritodani area in the Shinjo district of Mihama-cho. Lateral bendings of valleys along the fault in this area are clear geomorphological signatures of fault activity. We briefly report newly found multiple fault outcrops at these bending points with photos of them. This research is the result of joint research by Kansai Electric Power Company, University of Toyama, and JAEA.
Takai, Shizuka; Kimura, Hideo*; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Munakata, Masahiro; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-007, 174 Pages, 2020/09
The MIG2DF computer code is a computer program that simulates groundwater flow and radionuclide transport in porous media for the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The original version of MIG2DF was released in 1992. The original code employs a two-dimensional (vertical or horizontal cross-section, or an axisymmetric configuration) finite-element method to approximate the governing equations for density-dependent saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and radionuclide transport. Meanwhile, for geological disposal of radioactive wastes, landscape evolution such as uplift and erosion needs to be assessed as a long-term geological and climate events, considering site conditions. In coastal areas, the impact to groundwater flow by change of salinity distribution to sea level change also needs to be considered. To deal with these events in the assessment, we have revised the original version of MIG2DF and developed the external program which enables MIG2DF to consider unsteady landscape evolution. In these developments, this report describes an upgrade of MIG2DF (Version 2) and presents the configuration, equations, methods, and verification. This reports also give the explanation external programs of MIG2DF: PASS-TRAC (the particle tracking code), PASS-PRE (the code for dataset preparation), and PASS-POST (the post-processing visualization system).
Onoe, Hironori; Kosaka, Hiroshi*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yasue, Kenichi
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 26(1), p.3 - 14, 2019/06
In this study, it is focused on topographic changes due to uplift and denudation, also climate perturbations, a method which is able to assess the long-term variability of groundwater flow conditions using the coefficient variation based on some steady-state groundwater flow simulation results was developed. Spatial distribution of long residence time area which is not much influenced due to long-term topographic change and recharge rate change during the past one million years was able to estimate through the case study of the Tono area, Central Japan. By applying this evaluation method, it is possible to identify the local area that has low variability of groundwater flow conditions due to topographic changes and climate perturbations from the regional area quantitatively and spatially.
Ueki, Taro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(10), p.1180 - 1192, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)In Monte Carlo criticality analysis under material distribution uncertainty, it is necessary to evaluate the response of neutron effective multiplication factor (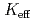 ) to the space-dependent random fluctuation of volume fractions within a prescribed bounded range. Normal random variables, however, cannot be used in a straightforward manner since the normal distribution has infinite tails. To overcome this issue, a methodology has been developed via forward-backward-superposed reflection Brownian motion (FBSRBM). Here, the forward-backward superposition makes the variance of fluctuation spatially constant and the reflection Brownian motion confines the fluctuation driven by normal noise in a bounded range. FBSRBM was implemented using Karhunen-Loeve expansion and applied to the fluctuation of volume fractions in a model of UO
) to the space-dependent random fluctuation of volume fractions within a prescribed bounded range. Normal random variables, however, cannot be used in a straightforward manner since the normal distribution has infinite tails. To overcome this issue, a methodology has been developed via forward-backward-superposed reflection Brownian motion (FBSRBM). Here, the forward-backward superposition makes the variance of fluctuation spatially constant and the reflection Brownian motion confines the fluctuation driven by normal noise in a bounded range. FBSRBM was implemented using Karhunen-Loeve expansion and applied to the fluctuation of volume fractions in a model of UO -concrete media with stainless steel.
-concrete media with stainless steel.
Takada, Shoji; Honda, Yuki*; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Sekita, Kenji; Nemoto, Takahiro; Tochio, Daisuke; Ishii, Toshiaki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Sawa, Kazuhiro*
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2018/10
Nuclear heat utilization systems connected to HTGRs will be designed on the basis of non-nuclear grade standards for easy entry of chemical plant companies, requiring reactor operations to continue even if abnormal events occur in the systems. The inventory control is considered as one of candidate methods to control reactor power for load following operation for siting close to demand area, in which the primary gas pressure is varied while keeping the reactor inlet and outlet coolant temperatures constant. Numerical investigation was carried out based on the results of nuclear heat supply fluctuation tests using HTTR by non-nuclear heating operation to focus on the temperature transient of the reactor core bottom structure by imposing stepwise fluctuation on the reactor inlet temperature under different primary gas pressures below 120C. As a result, it was emerged that the fluctuation absorption characteristics are not deteriorated by lowering pressure. It was also emerged that the reactor outlet temperature did not reach the scram level by increasing the reactor inlet temperature 10 C stepwise at 80% of the rated power as same with the full power case.
Ebara, Shinji*; Takamura, Hiroyuki*; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41(17), p.7139 - 7145, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:18.15(Chemistry, Physical)In this study, a flow visualization and pressure measurement were conducted by using an experimental setup including test sections of 1/7-scale models of the cold-leg piping of Japan sodium-cooled reactor with high Reynolds number region up to about one million. Regarding the flow field, flow separation appeared in the intrados of the third elbow. However, the separation region was smaller than that observed in the first elbow in the direction normal to the mean flow and was larger in the streamwise direction. This can be considered because of the swirling flow generated downstream of the second elbow which flowed into the third elbow with a little reduction. From the pressure fluctuation test, it was found that prominent frequencies of the pressure fluctuation appeared at about 0.4 in Strouhal number, which corresponds to a nondimensional frequency, in the region from 0 D to 0.4 D downstream of the elbow outlet, where D is the diameter of the piping. And weak peaks of about 0.7 in Strouhal number were observed in the region far 0.75 D downstream of the outlet.
Ebara, Shinji*; Takamura, Hiroyuki*; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Emerging Nuclear Energy Systems (ICENES 2015) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/10
In this study, a flow visualization and pressure measurement were conducted by using an experimental setup including test sections of 1/7-scale models of the cold-leg piping of Japan sodium-cooled reactor with high Reynolds number region up to about one million. Regarding the flow field, flow separation appeared in the intrados of the third elbow. However, the separation region was smaller than that observed in the first elbow in the direction normal to the mean flow and was larger in the streamwise direction. This can be considered because of the swirling flow generated downstream of the second elbow which flowed into the third elbow with a little reduction. From the pressure fluctuation test, it was found that prominent frequencies of the pressure fluctuation appeared at about 0.4 in Strouhal number, which corresponds to a nondimensional frequency, in the region from 0 D to 0.4 D downstream of the elbow outlet, where D is the diameter of the piping. And weak peaks of about 0.7 in Strouhal number were observed in the region far 0.75 D downstream of the outlet.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Tanaka, Masaaki; Iwamoto, Yukiharu*
Proceedings of ASME-JSME-KSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference 2015 (AJK 2015-FED) (USB Flash Drive), p.231 - 240, 2015/07
This paper intends to validate the numerical simulation tool, the U-RANS approach with the Reynolds Stress Model. It is a commercial computational fluid dynamics code using single short-elbow in the 1/10 and 1/3 scale water experiments simulating JSFR hot-leg piping. The numerical results agreed with their experimental data for time-averaged velocity distributions, flow field visualization, and power spectral densities of pressure fluctuation. U-RANS numerical simulation tool validated single short elbow flow applicable. Also, unsteady flow fields in the show elbow flow with a cyclic secondary flow and the subsequent horse shoe vortex were shown. The numerical simulation results with or without the IHX plenum at the outlet from the effect of the outlet condition did not show significant difference in terms of the time-averaged velocity distribution, pressure fluctuation power spectral density. Hence the effect of the outlet condition is assumed to be negligibly small.
Iwamoto, Yukiharu*; Kusuzaki, Ryo*; Sogo, Motosuke*; Yasuda, Kazunori*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of ASME-JSME-KSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference 2015 (AJK 2015-FED) (USB Flash Drive), p.1767 - 1773, 2015/07
Wall pressure measurements and flow visualization were conducted for a 90 degree elbow of which the axis curvature radius became the same as its inner diameter (125 mm). A deflected inflow, having an almost constant velocity slope, was introduced. Ensemble averaged pressure distributions showed no normalized pressure difference in cases of Reynolds numbers of 320,000 and 500,000. Comparisons with uniform inlet flow case proved; low-pressure region at the intrados of the elbow was weakened whereas a high pressure region outside strengthened in the deflected inflow case. Pressure distribution downstream of the elbow increased at the inside until two diameters downstream from the elbow exit. Flow visualization showed the pressure increase from collision of a strengthened secondary flow of extrados convection. The unsteady pressure distribution showed a circumferential extent of a strongly fluctuating region in and downstream the elbow decreased, comparing with the uniform inlet flow case.
Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Nakamura, Yasuo; Nakatani, Takayoshi
JAEA-Technology 2015-014, 34 Pages, 2015/06
[The article has been found to have a problem about reliability of the corrosion data acquisition, and thus it is unavailable to download the full text in accordance with authors' intentions to retract the report.] In order to dispose of radioactive wastes for sub-surface disposal, JAEA has studied the safety assessment for likely scenario and less-likely scenario. Radioactive nuclide leaching rate under the sub-surface disposal is important parameter in the safety assessment because radioactive nuclides in activated metal wastes are released with its corrosion. In this report, sensitivity of radioactive nuclide leaching rate is studied for the safety assessment. As the result, it is confirmed that Cl-36 which is dominant for the safety assessment in groundwater scenario is sensitive to radioactive nuclide leaching rate, but Nb-94 which is dominant in tunnel excavation scenario is not sensitive to radioactive nuclide leaching rate but to distribution coefficients in engineered barrier.
Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; Okano, Fuminori; Oshima, Katsumi*; Numazawa, Susumu*; Oga, Tokumichi; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
Heisei-16-Nendo Osaka Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Omori, Shunzo
Sangyo To Denki, (629), p.1 - 2, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Nakatani, Takeshi; Agui, Akane; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Takao, Masaru*; Takeuchi, Masao*; Aoyagi, Hideki*; Tanaka, Hitoshi*
JAERI-Tech 2004-013, 16 Pages, 2004/12
We observed two characteristic electron orbit fluctuations caused when the phase of ID23 (APPLE-2 type undulator) installed at SPring-8 was driven. One was caused by the variation of magnetic error filed of ID23 when the phase was driven. The other was caused by the noise from the phase drive system which adoped AC servomotors. We measured these orbit fluctuations synchronized with the phase motion using the real-time electron beam position measurement system. The part of the orbit fluctuation was supressed by the correction table which was made referring to the obtained data.
Takeda, Seiji; Minase, Naofumi; Kimura, Hideo
JAERI-Conf 2004-011, p.133 - 134, 2004/07
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Takuro; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi; Uno, Sadanori
Dai-16-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.80 - 83, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Nakatani, Takeshi; Agui, Akane; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Takao, Masaru*; Aoyagi, Hideki*; Takeuchi, Masao*; Tanaka, Hitoshi*
AIP Conference Proceedings 705, p.290 - 293, 2004/00
We have developed a new method to extract only the orbit fluctuation caused by changing magnetic field error of an insertion device (ID). This method consists of two main parts. (i) The orbit fluctuation is measured with modulating the error field of the ID by using the real-time beam position measuring system. (ii) The orbit fluctuation depending on the variation of the error field of the ID is extracted by the filter applying the Wavelet Transform. We call this approach the amplitude modulation method. This analysis technique was applied to measure the orbit fluctuation caused by the error field of APPLE-2 type undulator (ID23) installed in the SPring-8 storage ring. We quantitatively measured two kinds of the orbit fluctuation which are the static term caused by the magnetic field error and the dynamic term caused by the eddy current on the ID23 chamber.
Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Agui, Akane; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takao, Masaru*; Aoyagi, Hideki*; Takeuchi, Masao*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Tanaka, Hitoshi*
AIP Conference Proceedings 705, p.21 - 24, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Kuroda, Hiroshi*; Isoda, Yutaka*; Onishi, Mitsuyo*; Iwahashi, Masayuki*; Sato, Chizuru*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Ito, Toshimichi; Iseda, Kenichi*; Nishizawa, Keisuke*; Shima, Shigeki*; et al.
Umi No Kenkyu, 12(2), p.195 - 214, 2003/03
Variabilities of the periodical current fluctuations on the shelf in Hidaka Bay were examined with use of ferry-mounted ADCP data obtained during 2000-2001. As the result of analysis, (1) three periodical variations around 10-, 25- and 60-day period are found, (2) the horizontal phase lag of these variations is little along the ship track, and the vertical phase lag is little at 10- and 25-day variations while several-day at 60-day variation, and (3) the 10-day variation shows coherent cross-correlation between current and wind.
Shiina, Yasuaki; Komaki, Katsuya*; Tanaka, Gaku*; Hishida, Makoto*
JAERI-Tech 2001-076, 49 Pages, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Kato, Tomoko; ; Suzuki, Yuji*; ; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko; Ikeda, Takao*; Richard, L.*
JNC TN8400 2001-003, 128 Pages, 2001/03
In the safety assessment of a high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal system, it is required to estimate radiological impacts on future human beings arising from potential radionuclide releases from a deep repository into the surface environment. In order to estimate the impacts, a biosphere model is developed by reasonably assuming radionuclide migration processes in the surface environment and relevant human lifestyles. Releases from the repository might not occur for many thousands of years after disposal. Over such timescales, it is anticipated that the considerable climatic change, for example, induced by the next glaciation period expected to occur in around ten thousand years from now, will have a significant influence on the near surface environment and associated human lifestyles. In case of taking these evolution effects into account in modeling, it is reasonable to develop several alternative models on biosphere evolution systems consistent with possible future conditions affected by expected climatic changes. In this study, alternative biosphere models were developed taking effects of possible climatie change into account. In the modeling, different climatic states existing in the world from the present climate condition in Japan are utilized as an analogy. Estimation of net effects of the climatic change on biosphere system was made by comparing these alternative biosphere models with a constant biosphere model consistent with the present climatic state through flux to dose conversion factors derived from each one.